Plenary Speakers

Prof. Ray T. Chen
The University of Texas at Austin, USA
Title: Near- and Mid-IR Photonic Integrated Circuits (PICs) for Bio and Chemical Sensing, Interconnects and Computing with AI and ML Applications
Abstract:
The advancement of sensing, interconnects and computing is mainly from the R&D works on electrons and photons, which carry drastically different characteristics defining different technology roadmaps. Due to the saturation of the Moore’s law, the advantages of photon-based devices provide solutions with the unprecedented performance. In this talk, we will present the integrated photonic devices covering near and mid-IR wavelengths for biosensing, SERS and spectroscopy sensing for Methane, Nitrogen Dioxide, CO, Ethanol, Ammonia, and TEP. Mid-IR Lidar Chip centered at 4.6 micron will also presented.
Today’s fabrication of planar photonic circuits is reaching the limits of integration density. The minimum feature sizes are fundamentally limited by the wavelength (~1 µm) of light and the refractive index contrast achievable in the optical materials. By utilizing the unique feature of photons, which are Bosons by definition, we can further enhance the interconnectivity physically stacking optical waveguide layers without interference to significantly enhance the number of interconnects on one optical layer.
Silicon photonics for both digital and analog computing will be introduced with low latency, high bandwidth and multi-wavelength operations for AI and ML applications. Multiple photonic circuits were demonstrated to ensure low latency, high bandwidth and low energy consumption without compromising the machine learning accuracy. A myriad of data sets has been explored. And the details will be presented in the plenary talk.
Biography:
Ray T. Chen Graduated from TsingHua University in Taiwan with a B.S. degree in Physics in 1980. He received his PhD degree in EE from the University of California in 1988. He is currently a senior Endowed Chair Professor at The University of Texas Austin. His research work has been awarded over 150 research grants and contracts from such sponsors as Army, Navy, Space-Force, Air-Force, DARPA, MDA, NSA, NSF, DOE, EPA, NIST, NIH, NASA, Texas State, and private industry. Chen served as the CTO, Founder, and Chairman of the Board of Radiant Research, Inc. from 2000 to 2001, where he raised 18 million dollars A-Round funding to commercialize polymer-based photonic devices involving over twenty patents, which were acquired by Finisar in 2002, a publicly traded company in the Silicon Valley (NASDAQ:FNSR). He also serves as the founder and Chairman of the Board of Omega Optics Inc. since its initiation in 2001. Omega Optics has received over twenty million dollars in research funding from private sectors and government agencies.
He received the honorary citizenship award in 2003 from the Austin city council for his contribution in community service. He was also the recipient of the 2008 IEEE Teaching Award, and the 2010 IEEE HKN Loudest Professor Award. 2013 NASA Certified Technical Achievement Award for contribution on moon surveillance conformable phased array antenna. During his undergraduate years at the National Tsing Hua University, he led the 1979 university debate team to the National Championship of the Taiwan College-Cup Debate Contest.
Chen’s group at UT Austin has reported its research findings in more than 1,000 publications including over 100 invited papers and 82 patents. Chen is a Fellow of the National Academy of Inventors, IEEE, AIIA (International Artificial Intelligence Industry Alliance), Optica (OSA), and SPIE. Chen has supervised 41 postdocs and graduated 60 PhD students from his group. And many of them are professors in research universities in the USA and abroad.

Prof. Harald Giessen
University of Stuttgart, Germany
Title: 3D Printed Complex Microoptics: Fundamentals and First Benchmark Applications
Abstract:
We introduce 3d printed complex microoptics, spanning a range between a few micrometers up to 5 mm. Our lens system consists of aspherical multiplet lens systems which can give high numerical apertures with simultaneously excellent imaginag properties over the entire field of view, even directly on an optical fiber tip. Combining several printed materials with different refractive indices and dispersions and the combination with diffractive elements allows for realization of micro-optical achromats or even apochromats which are aplanatic (no first- and third-order aberrations such as spherical aberration, astigmatism, coma, distortion etc.) and achromatic for 3 wavelengths (red, green, blue). We also demonstrate the direct printing of black resists, which results in aperture stops and blackened hulls.
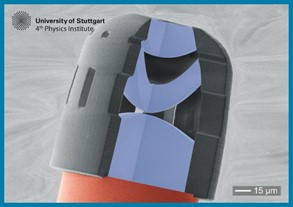
Atomic layer deposition yields antireflection coatings on all optical elements. Confocal surface profiling and wavefront interferometry demonstrate accuracies far better than lambda/20. In combination with high-resolution nanostructuring, also 3D holograms and metasurfaces can be included.
We utilize these methods to demonstrate the smallest endoscope in the world, being able to pass through a root canal of a tooth, as well as ultracompact sensors with hologon or hypergon lenses or a set of Scheimpflug lenses with nearly 2pi steradian imaging solid angle. Illumination systems as well as holographic projectors and beam shapers directly on optical fiber tips are demonstrated. Coupling single quantum emitters or single photon detectors to single mode fibers is demonstrated. Furthermore, single-fiber optical trapping of polystyrene beads, live cells, or atomic systems becomes a possibility.
Recently, we also demonstrated the use of 3D printed optics inside of a laser cavity, connecting a DBR mirror in a fiber with a solid state laser crystal.
Biography:
Harald Giessen graduated with a MSc in Physics from University of Kaiserslautern, Germany, and obtained his MSc and PhD in Optical Sciences in 1994 and 1995 from Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, working with Nasser Peyghambarian and Pierre Meystre. After a postdoc in 1996 at Max-Planck-Institute for Solid State Research in Stuttgart, Germany and an Assistant Professorship at University of Marburg, Germany, from 1997-2000 he became Associate Professor at University of Bonn, Germany. Since 2005 he is Full Professor and Director of the 4th Physics Institute and the Stuttgart Research Center of Photonics Engineering (SCoPE) at University of Stuttgart. His research deals with Ultrafast Nanooptics, Plasmonics, Metasurfaces and 3D Printed Micro-Optics. He is Fellow of Optica and has won an ERC Advanced Grant for Complex Plasmonics. In 2024, he was awarded the Robert-Wichard-Pohl Prize of the German Physical Society for his pioneering work of 3D Printed Micro-Optics. From 2018-2021 he was Highly Cited Researcher (Top 1%).

Prof. Baohua Jia
RMIT University, Australia
Title: Laser Nanoprinting of Atomaterials
Abstract:
This presentation mainly introduces the interaction between 3D nanoprinting and various materials at the atomic scale. Describe the precise and unparalleled manipulation of materials by nanoprinting at the spatial, temporal, and atomic scales. In particular, the application status and broad prospects of optical nanoprinting and two-dimensional photonic integrated devices are introduced in detail. The report will also share the future development directions of ultrafast optical nanoprinting and angstrom material devices, and the major challenges faced. The developed scalable graphene metamaterials show attractive optical and thermal properties. Through patterning with advanced laser nanoprinting technique, functional photonic devices with ultrathin, light weight and flexible nature have been demonstrated promising exciting opportunities for integrated photonics.
Biography:
Distinguished Professor Baohua Jia is a Fellow of Australian Academy of Technological Sciences and Technologies (FTSE), and Future Fellow at RMIT University, Australia. Before joining RMIT University in 2022, Baohua was a tenured professor at Swinburne University of Technology and Founding Director of Centre for Translational Atomaterials. Professor Jia is a Fellow of Optica (previously known as the Optical Society of America), and a Fellow of the Institute of Materials, Minerals and Mining (IMO3). Since 2019, Prof. Jia has served as a Colleague of Expert for the Australian Research Council. Professor Jia's research focuses on the design and optical characterization of novel nanostructures and nanomaterials, fabrication, and efficient conversion and storage of light energy. As a leading Chief Investigator, Professor Jia received a total of more than $50 million in research funding support. Professor Jia has published more than 350 journal papers with an h-index of 80 (Google Scholar) and developed more than 20 invention patents and patent applications. Based on Professor Jia's outstanding contributions in scientific research, she has won many awards, including the 2017 finalist of the Australian Prime Minister's Science Award, the Vice Chancellor's Industrial Achievement Award in 2011, 2016, and 2018, 2013, Young Science Leader Award, 2012 UNESCO L'Oréal Australia New Zealand Women in Science Award.

Prof. Jianping Yao
University of Ottawa, Canada
Title: Photonic Integrated Circuits: Pathway to Next-generation Microwave Photonic Systems
Abstract:
Photonic integrated circuits (PICs) provide compelling advantages for microwave photonic systems, including low loss, compact footprint, and high integration density, making them well-suited for next-generation microwave subsystems and systems. This talk will highlight recent advances in integrated microwave photonic systems enabled by PICs, with applications including true time delay networks for wideband beamforming, optoelectronic oscillators for low-phase-noise, high-frequency microwave generation, programmable signal processors for versatile photonic signal processing, and high-sensitivity optical sensors.
Biography:
Jianping Yao is a Distinguished University Professor and University Research Chair in the School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, University of Ottawa, Canada. He has been working in Microwave Photonics and has published 400+ peer-reviewed journal papers and 300+ conference papers, with 30,000+ citations and an H-index of 91. He served as Editor-in-Chief of IEEE Photonics Technology Letters from 2017 to 2021 and was an elected member of the IEEE Photonics Society Board of Governors from 2018 to 2021. He was Chair of the IEEE MTT-S Microwave Photonics Technical Committee from 2016 to 2021 and was an IEEE Distinguished Microwave Lecturer from 2013 to 2015. He received the IEEE R.A. Fessenden Award in 2018 and the IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques Society Microwave Applications Award in 2025. Dr. Yao is a Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering (2012), the Royal Society of Canada (2018), IEEE (2012), and Optica (2010).

Prof. Xiaogang Peng
Zhejiang University, China
Title: Strongly- and Weakly-confined Semiconductor Nanocrystals as a Platform for Photon Manipulation
Abstract:
Strongly-confined semiconductor nanocrystals are known as quantum dots, which have received great attention in the recent years as optical and optoelectronic materials. Here, we show that weakly-confined semiconductor nanocrystals offer a much greater platform than quantum dots do for photon manipulation with their unique dynamic excitons as the medium. Experimental results confirm that the photo- or electro-generated electron-hole pairs in weakly-confined semiconductor nanocrystals are neither free carriers nor Wannier excitons. Instead, with weak electrostatic interaction between an electron and hole, either carrier is spatially confined by the lattice-ligands boundary, which is better described as a dynamic exciton. Different from a Wannier exciton, behaviour of a dynamic exciton can be readily tuned by the size, shape, and composition of a nanocrystal, making monodisperse semiconductor nanocrystals—both strongly- and weakly-confined—as optimal materials for optoelectronics.
Biography:
Xiaogang Peng is currently a Professor at Zhejiang University. Before moving back to China in 2009, he was on the faculty at the University of Arkansas as Assistant Professor (1999-2003), Associate Professor (2003-2005), and Professor with Chair (2005-2009). He received his B.S. (1987) and Ph.D. (1992) from Jilin University, China. His Postdoctoral experience followed by a position as Staff Scientist at UC Berkeley between 1994 and 1999 brought him into the field of colloidal nanocrystals. Shortly after starting his tenure at the University of Arkansas in 1999, he founded NN-Labs LLC in USA to explore industrial applications of quantum dots. In 2009, he founded Najing Tech Corporation in Hangzhou, currently focusing on quantum-dot display technologies.

Prof. Hong-Bo Sun
Tsinghua University, China
Title: Femtosecond Laser Nano-Fabrication, an Enabling Technology for 3D Optoelectronic Integration
Abstract:
Femtosecond laser nanofabrication provides a new technical avenue towards micro-nanodevices. Comparing with the currently available nanofabrication approaches including photolithography, nanoimprinting, focus ion beam, it is unique in the three-dimensional (3D) processing capability and applicability to various materials. These make the new concept, stereo-integrated photonics circuits possible. The talk will introduce our recent research progress along these lines, from light-matter interaction physics to new concept optoelectronic devices working from the visible to infrared wave ranges.
Biography:
Hong-Bo Sun, received the B.S. and the Ph.D degrees in electronics from Jilin University, Changchun, China, in 1992 and 1996, respectively. He worked as a postdoctoral researcher in Satellite Venture Business Laboratory, the University of Tokushima, Japan, from 1996 to 2000, and then as an assistant professor in Department of Applied Physics, Osaka University, Japan. In 2004, he was promoted as a full professor (Changjiang Scholar) in Jilin University, and since 2017 he has been working in Tsinghua University, China. His research interests have been focused on laser precision manufacturing. He has published over 500 papers, which have been cited for over 40000 times, and H factor is 101, according to ISI search report. He is currently the executive editor-in-chief (EEIC) of Light: Science and Applications and editor-in-chief of PhotoniX (Both from Nature Publishing Group). He is IEEE, OSA and SPIE fellow.

Dr. Haoshuo Chen
Nokia Bell Labs, USA
Title: Innovations and Challenges: The Next Frontier in Space-division Multiplexing
Abstract:
Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) research has significantly advanced the field of high-capacity transmission in optical communications. By leveraging multiple spatial channels within a single optical fiber, SDM has demonstrated the potential to exponentially increase data throughput, effectively addressing the growing demand for bandwidth in modern communication networks. Key achievements in SDM research have led to record-breaking transmission capacities, with experimental setups achieving petabit-per-second data rates over long distances. Additionally, advancements in digital signal processing (DSP) and spatial multiplexing techniques have enhanced the efficiency and reliability of SDM systems.
This talk will first focus on optical transceiver integration, introducing innovative designs for optical coherent receiver arrays. These arrays leverage surface-normal dual-polarization 90-degree optical hybrid arrays to support simultaneous space- and wavelength-division multiplexing. The coherent receiver array, capable of simultaneously detecting multiple spatial and wavelength channels, has been experimentally validated for space- and wavelength-division multiplexing reception in two-core fiber systems.
Next, the talk will cover spatial switching, which is essential for future large-scale SDM systems. We will discuss an artificial intelligence (AI)-powered mobile robot capable of performing multiple network operation tasks such as fiber manipulation and switching. By employing the robot and real-time coherent receiver-based polarization sensing, we demonstrate an automated fiber switch with network path verification.
Lastly, we will explore the potential application of large language models to further enhance SDM fiber designs, opening new avenues for innovation and optimization in this rapidly evolving field.
Biography:
Dr. Haoshuo Chen received his Ph.D. degree (Cum Laude) in Electrical Engineering from Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/E), The Netherlands, in 2014. Since December 2014, he has been a member of the technical staff at Nokia Bell Labs, Murray Hill, NJ, USA. Dr. Chen has (co-)authored over 300 journal and conference papers, including more than 30 post-deadline papers, and holds over 15 US patents. Dr. Chen has served as an Associate Editor of the IEEE Journal of Quantum Electronics, a strategy representative of the IEEE Photonics Society Globalization Committee, and Program Chair of the 28th Optoelectronics and Communications Conference (OECC). Additionally, he has served as a subcommittee chair/member and workshop organizer at major photonic conferences such as OFC, ECOC, OECC, ICOCN, IPC, ACP, APC, CLEO/PR, and SUM. His primary research interests include space-division multiplexing, dense photonic integration, power-efficient digital signal processing, fiber components, and wavelength/space switches.


